What is pancreatic cancer?
Pancreatic cancer is a 6-inch long organ situated behind the stomach in the midsection’s rear, close to the nerve bladder. It contains organs that make pancreatic juices, hormones, and insulin. Malignancy can influence either the endocrine or the exocrine organs in the pancreas. The exocrine organs produce juices, or catalysts, that enter the digestion tracts and help digest fat, proteins, and starches. These make up the more significant part of the pancreas. The endocrine organs are little bunches of cells known as the islets of Langerhans. They discharge the hormones insulin and glucagon into the circulatory system. There, they oversee glucose levels. At the point when they are not working appropriately, the outcome is frequently diabetes.
Types
There are two distinct kinds of malignant pancreatic growth, contingent upon whether it influences the exocrine or endocrine capacities. They have diverse danger factors, causes, indications, analytic tests, medicines, and viewpoints. Exocrine pancreatic disease Tumors that influence exocrine capacities are the most well-known sort. They can be harmful or considerate. Kindhearted tumors or growths are called cystadenomas. Most pancreatic tumors are threatening or harmful. Various sorts of pancreatic diseases can influence exocrine capacities. Sorts of tumor include:
- adenocarcinomas, which commonly start in organ cells in the channels of the pancreas
- acinar cell carcinoma, which begins in the pancreatic protein cells
- ampullry malignant growth, which begins where the bile pipe and pancreatic pipe meet the duodenum of the small digestive system.
- adenosquamous carcinomas
- squamous cell carcinomas
- monster cell carcinomas
Endocrine pancreatic malignant growth
Tumors that influence the endocrine elements of the pancreas are called neuroendocrine or islet-cell tumors. These are genuinely unprecedented. The name originates from the sort of hormone-delivering cell where the disease begins.
They include:
- insulinomas (insulin)
- glucagonomas (glucagon)
- gastrinomas (gastrin)
- somatostatinomas (somatostatin)
- VIPomas (vasoactive intestinal peptide or VIP)
Working islet cell tumors keep on making hormones. Non-working ones don’t. The more significant part of these tumors is amiable, yet non-working tumors are bound to be harmful, islet-cell carcinomas.
Malignancy can influence either the endocrine or the exocrine organs in the pancreas. The endocrine organs are little bunches of cells known as the islets of Langerhans. They discharge the hormones insulin and glucagon into the circulatory system. There, they oversee glucose levels. At the point when they are not working appropriately, the outcome is frequently diabetes. Also checkout the latest health news in USA.
Causes and risk factors
Scientists don’t know precisely why uncontrolled cell development occurs in the pancreas, yet they have distinguished some conceivable danger factors.
Genetic factors
Harm or changes in an individual’s DNA can prompt harm in the qualities that control cell division.
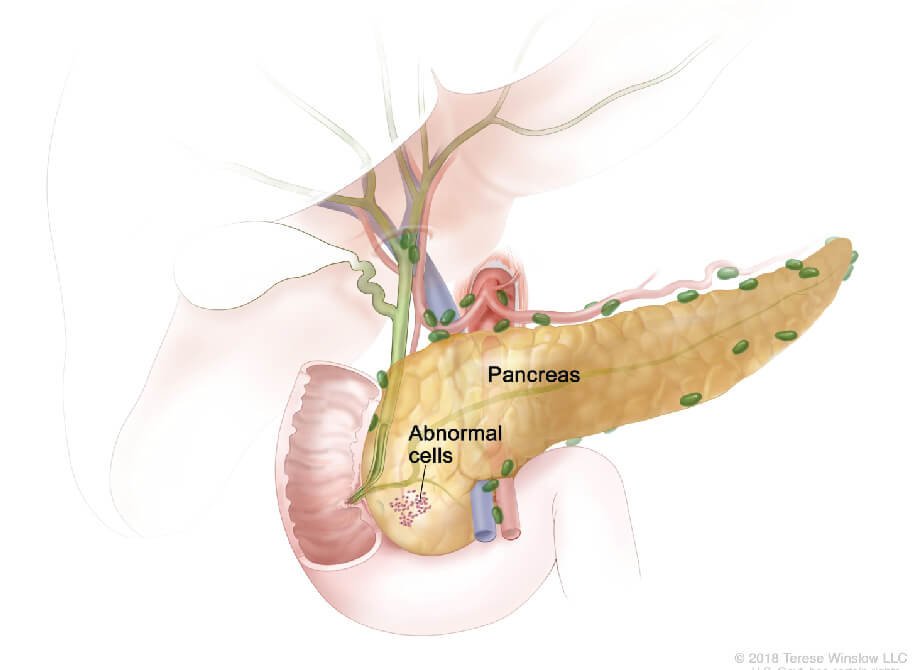
Innate hereditary changes go down through a family. There is proof that malignant pancreatic growth can run in families. Other hereditary changes happen on account of the introduction to an ecological trigger, for instance, tobacco. An individual with a specific hereditary disorder is bound to create pancreatic malignancy.
These include:
- innate bosom and ovarian malignancy condition
- melanoma
- pancreatitis
- non-polyposis colorectal malignant growth (Lynch disorder)
Sex
Pancreatic tumors influence men than regularly than ladies.
This year, the American Cancer Society expects that 29,200 men and 26,240 ladies will get a determination of pancreatic disease.
Environmental toxins

Substances that may expand the danger of pancreatic malignancy incorporate indeed:
- pesticides
- dyes
- synthetic substances utilized in metal refining
At the point when the body comes into contact with a cancer-causing agent, free revolutionaries structure. These harm cells and influence their capacity to work typically. The outcome can be harmful developments.
Other medical factors
Age is a significant danger factor, particularly after the age of 60 years. Researchers have additionally discovered a connection between malignancy of the pancreas and a few different sicknesses.
Other medical factors
- cirrhosis or scarring of the liver
- contamination of the stomach with the ulcer-causing microscopic organisms, Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
- diabetes mellitus
- persistent pancreatitis, or irritation of the pancreas
- gum disease or periodontal ailment
Life style factors
Some way of life variables may build the danger:
- smoking cigarettes or introduction to tobacco smoke
- overabundance weight and an absence of activity
- an eating routine that is high in red meat and fat and low in leafy foods
- long haul, weighty utilization of liquor, which can prompt ongoing pancreatitis, a danger factor for pancreatic malignancy
Pancreatic cancer Symptoms
Pancreatic malignant growth is frequently called a “quiet” ailment since manifestations don’t show until the later stages.
Tumors of the pancreas malignant growths are generally too little to even think about causing manifestations, and later indications are frequently vague. However, when the malignant growth develops, there might be:
- torment in the upper mid-region as the tumor pushes against nerves
- Jaundice, when issues with the bile pipe and liver lead to an effortless yellowing of the skin and eyes and obscuring of the pee.
- loss of craving, sickness, and regurgitating
- colossal weight reduction and shortcoming
- pale or dark greasy stool
However, various illnesses can cause similar manifestations, so a specialist can regularly not analyze pancreatic cancer malignancy until the later stages.
Other potential signs and indications include:
- Trousseau’s sign, when unconstrained blood clusters structure in the gateway veins, profound veins of the arms and legs, or other shallow veins
- clinical melancholy, which individuals here and there report before a finding
Islet cell or neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas may make the pancreas produce a lot of insulin or hormones.
The individual may insight:
- weakness or dizziness
- chills
- muscle spasms
- diarrhea
Pancreatic cancer malignant growth shows up in an unexpected way, contingent upon which part of the pancreas the tumor is in, regardless of whether the “head” or the “tail.”
Tumors at the last part are bound to bring about torment and weight reduction. At the opposite end, head tumors cause greasy stools, weight reduction, and jaundice.
In the event that the disease spreads, or metastasizes, new side effects can happen in the influenced territory and the remainder of the body.
When to see a Doctor pancreatic cancer
Side effects of pancreatic cancer malignancy regularly don’t show up until the later stages. On the off chance that you experience jaundice or some other unordinary side effects, you should see a doctor.
On the off chance that somebody in the family has just had pancreatic cancer malignant growth, or on the off chance that you have any of the danger factors and are worried about the chance of creating it, you ought to likewise address a specialist. They may propose screening.
Pancreatic cancer Diagnosis
A doctor will get some information about indications, take a family and clinical history, and complete a physical assessment. They will most likely additionally suggest a few tests.
Assessing symptoms
The doctor will give extraordinary consideration to regular indications, for example,
- stomach or back torment
- weight reduction
- helpless appetite
- tiredness
- irritability
- stomach related issues
- gallbladder amplification
- blood clumps, profound venous apoplexy (DVT), or aspiratory embolism
- greasy tissue anomalies
- diabetes
- expanding of lymph hubs
- looseness of the bowels
- steatorrhea, or greasy stools
- jaundice
A typical diabetes mellitus, Trousseau’s sign, and late pancreatitis may likewise be signs that pancreatic cancer malignant growth is available.
Laboratory test pancreatic cancer
Potential tests include:
- blood tests
- urine tests
- stool tests
Blood tests can recognize a compound that pancreatic disease cells discharge into the blood. Liver capacity tests check for bile channel blockage.
Imaging Tests of pancreatic cancer
The doctor may demand imaging tests to recognize if a tumor is available, and, provided that this is true, to perceive how far the disease has spread.
Regular imaging tests include:
- ultrasound or endoscopic ultrasound
- CT, MRI, or PET outputs
- X-beams, potentially with a barium supper
- an angiogram
Biopsy
This can affirm a finding. The specialist eliminates a little example of tissue for assessment under the magnifying lens.
Stages of pancreatic cancer
Next, the doctor will survey the malignancy phase, or how far the disease has spread, to figure out which treatment choices are appropriate.
The stage relies upon:
- the size and direct degree of the essential tumor
- how far the disease has spread to close by lymph hubs
- regardless of whether the disease has metastasized or spread to different organs in the body
The stages range from stage 0 to arrange IV.
Stage 0: There are carcinogenic cells in the top layers of pancreatic channel cells. They have not attacked other tissues or spread outside of the pancreas.
Stage IV: The malignant growth has spread too far off destinations all through the body.
At stage 0, effective treatment is conceivable. At stage IV, tumors have spread too far off organs. A specialist would prescribe medical procedures to ease torment or unblock channels.
Treatment
Disease treatment relies upon an assortment of components:
- the sort of cancer
- the phase of the disease
- the individual’s age, wellbeing status, and different attributes
- the person’s very own decisions
Medical procedure, radiation, and chemotherapy are the most widely recognized therapy alternatives.
The point of treatment is to:
- Remove the cancer
- relieve painful symptoms