Benign or Malignant: Understanding the Key Differences and What They Mean for Your Health
When it comes to health, one of the most common concerns people face is discovering a lump, growth, or tumor and wondering: is it benign or malignant? The distinction between these two terms is critical because it determines whether the condition is harmless or potentially life-threatening. Understanding the differences, the signs, and the next steps can reduce anxiety and help you make informed decisions about treatment.
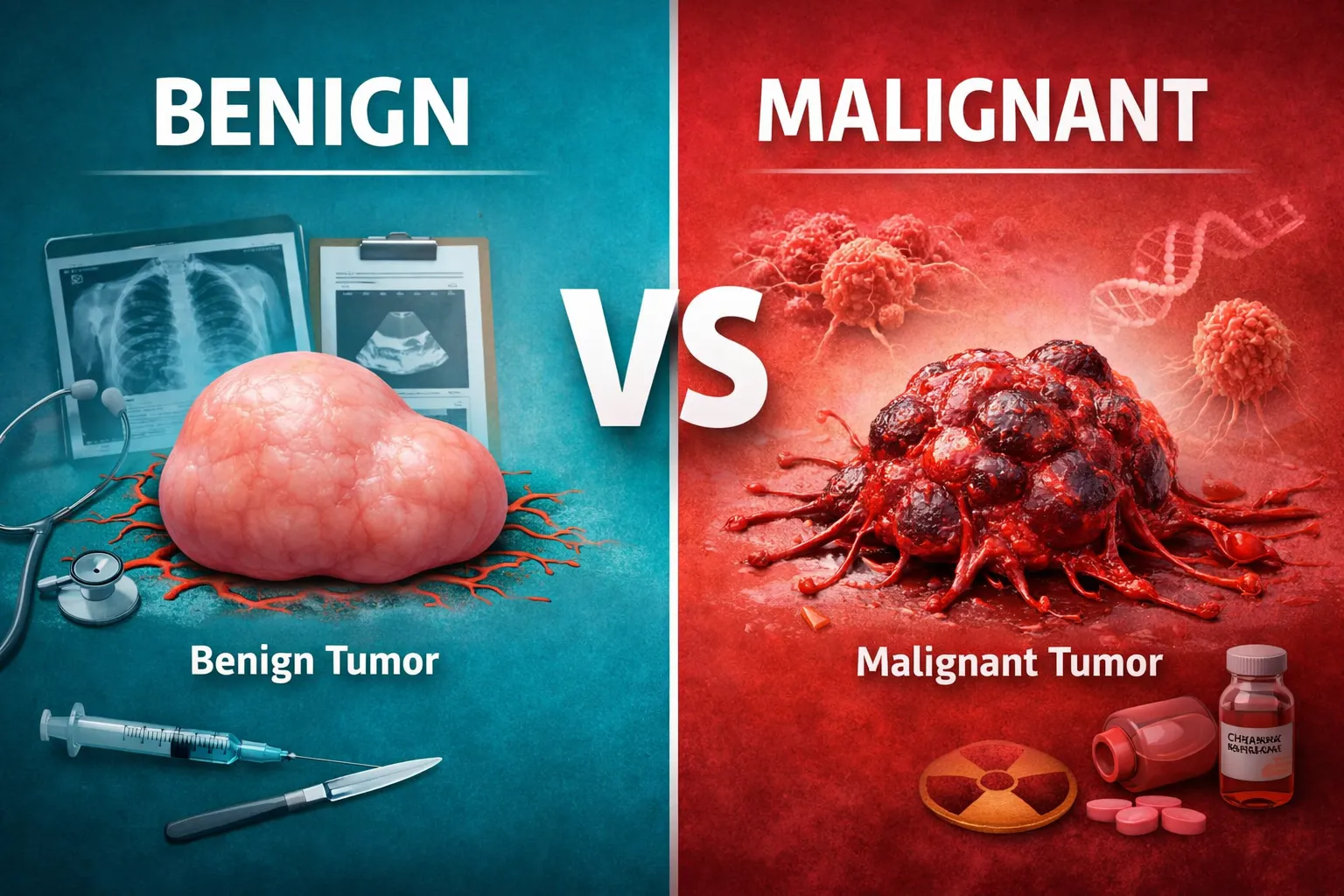
In simple terms, benign tumors are non-cancerous and usually slow-growing, posing minimal risk to your health. On the other hand, malignant tumors are cancerous, tend to grow aggressively, and can spread to other parts of the body. Knowing which category a growth falls into is crucial for timely treatment and long-term health.
What Does Benign Mean?
A benign tumor refers to a growth of cells that remains localized and does not invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors can appear in various organs, including the skin, breast, brain, and liver. While benign tumors are generally not life-threatening, they can sometimes cause problems depending on their size and location.
Key Characteristics of Benign Tumors
- Slow growth: Benign tumors grow gradually over time.
- Localized: They stay confined to one area and do not metastasize (spread).
- Smooth borders: Often have clear edges that make them easier to remove surgically.
- Low recurrence risk: Once removed, benign tumors rarely come back.
- Minimal symptoms: Many benign tumors don’t cause noticeable symptoms unless they press on nerves or organs.
Examples of benign tumors include:
- Lipomas (fatty lumps under the skin)
- Fibroids (common in the uterus)
- Adenomas (glands in the liver, colon, or thyroid)
- Hemangiomas (blood vessel growths, often in infants)
Even though benign tumors are not cancerous, they may require treatment if they interfere with normal organ function or cause discomfort.
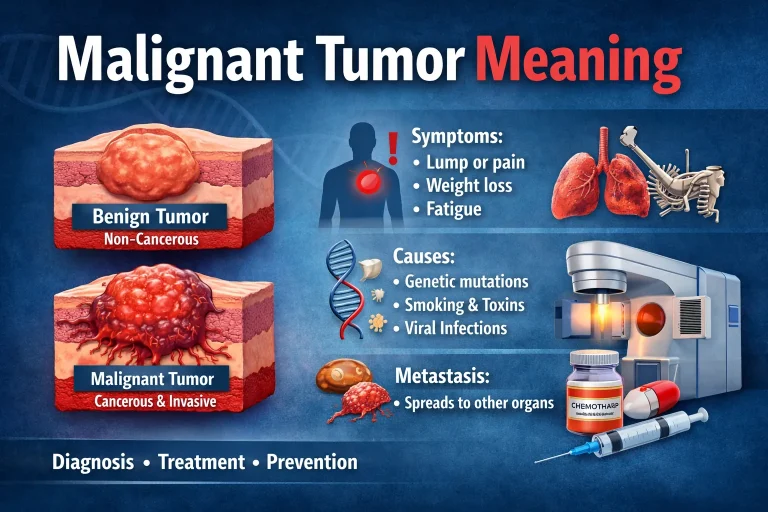
What Does Malignant Mean?
A malignant tumor is cancerous. Unlike benign tumors, malignant cells grow uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues, and can spread (metastasize) to distant organs. Malignant tumors are far more serious and require immediate medical attention.
Key Characteristics of Malignant Tumors
- Rapid growth: Malignant tumors grow quickly and can change in size over a short period.
- Invasion: They can invade surrounding tissues and organs, disrupting normal function.
- Potential to metastasize: Cancer cells can travel through blood or lymphatic systems to other parts of the body.
- Irregular borders: Often appear jagged or uneven, which can make removal more complicated.
- Symptoms: Can include pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and noticeable lumps.
Common types of malignant tumors include:
- Carcinomas (affecting skin, lungs, colon, or breast)
- Sarcomas (affecting bones, muscles, or connective tissues)
- Leukemia (cancer of blood-forming tissues)
- Lymphoma (affecting lymph nodes)
Malignant tumors often require aggressive treatment, such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of therapies, depending on the cancer type and stage.
Benign vs Malignant: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Understanding the differences between benign and malignant tumors is easier when you compare them directly:
| Feature | Benign | Malignant |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Slow | Rapid |
| Spread | Localized | Can metastasize |
| Borders | Smooth, defined | Irregular, poorly defined |
| Recurrence | Rare | Possible, even after treatment |
| Risk to Life | Usually low | High if untreated |
| Symptoms | Often minimal | Can be severe and systemic |
| Treatment | Observation or surgical removal | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy |
Common Signs That a Growth Might Be Malignant
While only a biopsy or medical imaging can definitively determine if a tumor is benign or malignant, certain warning signs may indicate malignancy:
- Rapid growth of a lump or mass
- Pain or tenderness in the area of the growth
- Changes in skin or tissue over the growth, such as discoloration or ulceration
- Unexplained weight loss or fatigue
- Persistent fever or night sweats
- Swelling of lymph nodes near the growth
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly for evaluation. Early detection dramatically increases the success of treatment.
How Doctors Determine If a Tumor Is Benign or Malignant
Medical professionals use a combination of tools to determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant:
1. Physical Examination
Doctors assess the tumor’s size, shape, mobility, and tenderness. Some characteristics, like smooth and movable lumps, often suggest a benign tumor.
2. Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound: Useful for examining soft tissue lumps, particularly in the breast or thyroid.
- CT Scan or MRI: Provide detailed images of internal tumors and can detect invasion of nearby tissues.
- X-rays: Commonly used for bone tumors.
3. Biopsy
A biopsy is the gold standard. It involves taking a small sample of the tissue to examine under a microscope. Pathologists look for:
- Cell appearance and structure
- Rate of growth
- Signs of invasion or metastasis
4. Blood Tests and Tumor Markers
Some cancers release specific markers into the blood, helping doctors differentiate between benign and malignant conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on whether a tumor is benign or malignant, its size, location, and potential complications.
Benign Tumors
- Observation: Many benign tumors don’t need treatment and can be monitored over time.
- Surgical Removal: If the tumor causes pain, functional issues, or cosmetic concerns.
- Medication: Rarely, certain benign tumors can shrink with medication (e.g., hormone therapy for fibroids).
Malignant Tumors
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor and possibly surrounding tissue to prevent recurrence.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill or slow the growth of cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: Advanced treatments that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
Preventive Measures and Early Detection
While not all cancers are preventable, early detection improves outcomes significantly. Here’s how you can stay proactive:
- Regular Check-Ups: Annual physicals and screenings based on age and risk factors.
- Self-Exams: For example, breast or testicular self-exams can detect lumps early.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking reduce cancer risk.
- Vaccinations: Vaccines like HPV can prevent cancers caused by viruses.
- Prompt Medical Attention: Don’t ignore unusual lumps, persistent pain, or unexplained symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a benign tumor turn malignant?
Most benign tumors remain non-cancerous, but a small percentage, such as certain types of polyps or moles, can become malignant over time. Regular monitoring is key.
Is all cancer malignant?
Yes, by definition, cancer refers to malignant growths that invade tissue and can spread to other parts of the body.
How long does it take to know if a tumor is benign or malignant?
With imaging and biopsy, doctors can usually provide answers within a few days to a week. The exact timing depends on the type of test and lab processing.
Are benign tumors dangerous?
Usually, they are not life-threatening. However, if they press on organs, nerves, or blood vessels, they can cause complications and may need surgical removal.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between benign or malignant growths is vital for your health. Benign tumors are generally harmless and slow-growing, whereas malignant tumors are aggressive and require immediate attention. Paying attention to warning signs, undergoing regular screenings, and seeking timely medical evaluation can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
If you notice unusual lumps, persistent pain, or unexplained symptoms, don’t delay early detection is your best defense. Knowing whether a growth is benign or malignant empowers you to make informed decisions, reduce anxiety, and take control of your health.
More here : Benign Tumor and Malignant Tumor Difference: Everything You Need to Know