UV VIS: Complete Guide to UV-Vis Spectroscopy, Uses, and Working Principle
UV VIS (ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy) is an analytical technique used to measure how much ultraviolet and visible light a substance absorbs. It helps identify chemical compounds, determine concentration levels, and analyze molecular structure. Scientists, laboratories, and industries rely on UV VIS to test water quality, pharmaceutical products, food safety, and environmental samples. If someone needs a reliable way to study chemical substances quickly and accurately, this spectroscopy is one of the most trusted and widely used methods.
What is UV VIS?
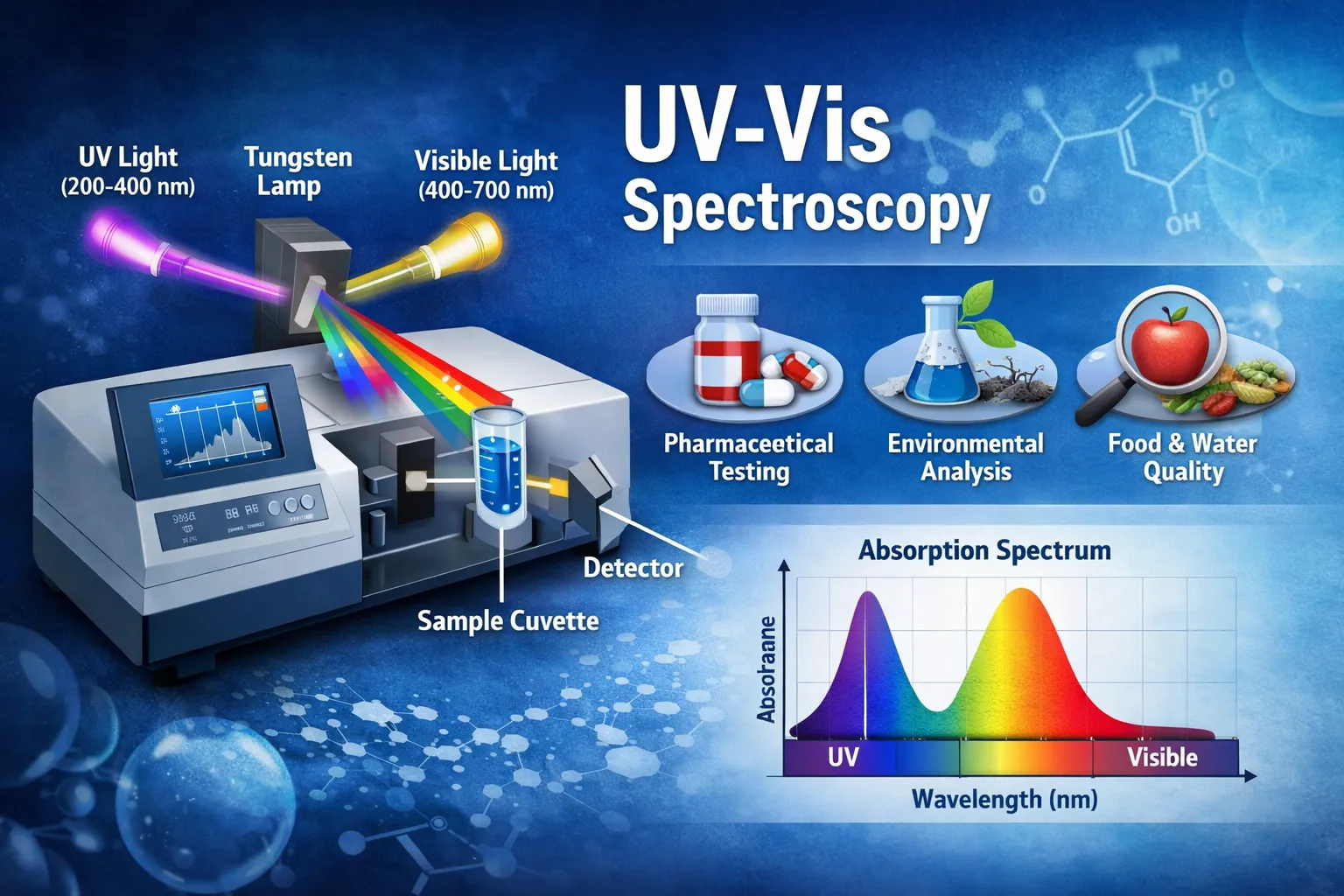
UV VIS refers to UV-Visible spectroscopy, a technique that studies how materials interact with ultraviolet light (200–400 nm) and visible light (400–700 nm). When light passes through or reflects off a sample, certain wavelengths are absorbed. The absorbed light provides information about the substance’s chemical composition and concentration.
UV VIS spectroscopy works based on the principle that molecules absorb light at specific wavelengths depending on their structure. This absorption creates a measurable spectrum that scientists use to identify or quantify substances.
Key Features of UV VIS Spectroscopy
- Measures absorption of UV and visible light
- Provides quantitative and qualitative chemical analysis
- Fast and non-destructive testing method
- Widely used across multiple scientific fields
- Requires minimal sample preparation
How this Spectroscopy Works
UV VIS spectroscopy operates through a simple but powerful process. A this spectrophotometer sends light through a sample, and the instrument measures how much light is absorbed.
Step-by-Step Working Principle
1. Light Source
The UV VIS instrument contains two light sources:
- Ultraviolet lamp for UV range analysis
- Tungsten or halogen lamp for visible light
2. Monochromator
The monochromator separates light into specific wavelengths. It allows the instrument to test one wavelength at a time.
3. Sample Holder (Cuvette)
The sample is placed inside a transparent container called a cuvette. Light passes through the sample, and absorption occurs depending on chemical properties.
4. Detector
The detector measures the amount of light that passes through the sample and converts it into electrical signals.
5. Data Output
The spectrophotometer produces a graph called an absorption spectrum, which shows the relationship between wavelength and absorbance.
Why UV VIS is Important in Modern Science
this spectroscopy plays a critical role in chemical and biological analysis. It allows scientists to measure concentration accurately and identify unknown substances.
Major Benefits of UV VIS
- Provides fast analytical results
- Offers high accuracy and reliability
- Supports real-time monitoring
- Requires small sample quantities
- Useful for both research and industrial applications
Because of these advantages, This is remains one of the most commonly used spectroscopic methods worldwide.
Applications of UV VIS Spectroscopy
UV VIS has diverse applications across industries, research laboratories, and healthcare sectors. The technology helps ensure safety, quality, and scientific accuracy.
Pharmaceutical Industry
This is widely used in drug development and quality control.
Common pharmaceutical uses include:
- Measuring drug concentration
- Testing chemical stability
- Identifying active ingredients
- Monitoring reaction processes
Pharmaceutical companies rely heavily on this spectroscopy to ensure medication safety and consistency.
Environmental Testing
Environmental laboratories use UV VIS to monitor pollutants and water quality.
Examples include:
- Detecting heavy metals
- Measuring nitrate and phosphate levels
- Monitoring wastewater treatment
- Testing air pollution samples
UV VIS helps governments and organizations maintain environmental safety standards.
Food and Beverage Industry
Food manufacturers use UV VIS analysis to ensure product quality and safety.
Typical applications include:
- Detecting food additives
- Measuring vitamin concentration
- Checking contamination levels
- Monitoring beverage color consistency
Clinical and Medical Laboratories
Medical labs depend on UV VIS spectroscopy for diagnostic testing and biological research.
Common medical uses include:
- Blood analysis
- Protein concentration measurement
- Enzyme activity testing
- DNA and RNA analysis
Chemical Research and Academic Studies
Researchers use UV VIS to study molecular structure and chemical reactions. The technique helps scientists understand reaction kinetics and material properties.
Components of a UV VIS Spectrophotometer
A UV VIS spectrophotometer contains several essential parts that work together to analyze samples accurately.
Main Instrument Components
Light Source
Provides UV and visible radiation for sample testing.
Monochromator
Filters light into specific wavelengths.
Sample Compartment
Holds the cuvette containing the test sample.
Detector
Measures transmitted light and converts it into readable data.
Data Processing System
Displays absorption results and spectrum graphs.
Each component plays a vital role in delivering accurate spectroscopic analysis.
Types of UV VIS Instruments
Different types of UV VIS spectrophotometers are available depending on analytical needs.
Single Beam Spectrophotometer
- Uses one light beam
- Simple and cost-effective
- Requires manual calibration
Double Beam Spectrophotometer
- Splits light into sample and reference beams
- Provides higher accuracy
- Reduces measurement errors
Diode Array Spectrophotometer
- Captures multiple wavelengths simultaneously
- Faster analysis
- Ideal for research laboratories
Understanding UV VIS Absorption Spectrum
The UV VIS absorption spectrum displays how a sample absorbs light across different wavelengths. The spectrum provides valuable chemical information.
Key Terms in UV VIS Spectrum
- Absorbance: Amount of light absorbed by the sample
- Transmittance: Amount of light passing through the sample
- Wavelength: Distance between light waves measured in nanometers
- Chromophore: Molecule part responsible for light absorption
Scientists use these values to calculate substance concentration using Beer-Lambert Law.
Beer-Lambert Law in UV VIS Analysis
Beer-Lambert Law explains the relationship between light absorption and sample concentration.
Formula:
A = ε × l × c
Where:
- A = Absorbance
- ε = Molar absorptivity
- l = Path length
- c = Concentration
This law allows accurate determination of unknown sample concentrations using UV VIS spectroscopy.
Advantages of UV VIS Spectroscopy
UV VIS provides several practical benefits compared to other analytical techniques.
Major Advantages
- High sensitivity and precision
- Quick measurement process
- Low operational cost
- Minimal sample preparation
- Suitable for liquids and solutions
- Non-destructive testing
Because of these benefits, this is widely used in quality control laboratories.
Limitations of UV VIS Spectroscopy
Although this is highly useful, it has certain limitations that users should consider.
Common Limitations
- Less effective for solid samples
- Overlapping absorption peaks may occur
- Requires transparent solvents
- Cannot always identify complex mixtures
Understanding these limitations helps users select the correct analytical technique for their needs.
Factors Affecting UV VIS Accuracy
Several factors influence UV VIS measurement accuracy. Proper control of these variables improves results.
Important Accuracy Factors
- Sample purity
- Cuvette cleanliness
- Instrument calibration
- Solvent selection
- Temperature control
Maintaining proper testing conditions ensures reliable spectroscopic data.
UV VIS vs Other Spectroscopic Techniques
This spectroscopy is often compared with other analytical techniques like infrared spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy.
UV VIS vs Infrared Spectroscopy
| Feature | UV VIS | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| Measures | Electronic transitions | Molecular vibrations |
| Sample Type | Liquids and solutions | Solids and gases |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Complexity | Simple operation | Requires detailed interpretation |
UV VIS vs Fluorescence Spectroscopy
- UV VIS measures absorption of light
- Fluorescence spectroscopy measures emitted light
- This works for concentration analysis
- Fluorescence offers higher sensitivity for trace detection
Both techniques complement each other in advanced research.
Real-World Examples of UV VIS Usage
This is spectroscopy supports daily industrial and scientific processes.
Example 1: Water Quality Testing
Municipal laboratories use UV VIS to detect contaminants in drinking water.
Example 2: Pharmaceutical Drug Testing
Manufacturers measure drug purity using UV VIS absorption analysis.
Example 3: Agricultural Chemical Testing
This is helps analyze pesticide and fertilizer concentrations.
How to Use a UV VIS Spectrophotometer Properly
Following correct procedures ensures accurate and consistent results.
Best Practices
- Calibrate the instrument before testing
- Use clean and scratch-free cuvettes
- Select appropriate solvent and wavelength
- Prepare samples carefully
- Record baseline measurements
Proper technique improves reliability and reduces measurement errors.
Emerging Trends in UV VIS Technology
This spectroscopy continues evolving with modern scientific advancements.
Latest Developments
- Portable UV VIS spectrophotometers
- Automated sample analysis systems
- AI-integrated spectroscopic data analysis
- High-speed diode array detection
These innovations make UV VIS technology faster, more accurate, and easier to use in field testing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does UV VIS measure?
This is measures how much ultraviolet and visible light a sample absorbs to determine chemical properties and concentration.
Is UV VIS spectroscopy destructive?
No, this is a non-destructive analytical method.
What industries use UV VIS?
Pharmaceutical, environmental, medical, food, chemical, and academic research industries use UV VIS spectroscopy.
Can this detect unknown compounds?
Yes, UV VIS can help identify unknown compounds based on absorption spectrum patterns.
When Should You Use UV VIS Spectroscopy?
UV VIS is ideal when:
- Measuring concentration of solutions
- Studying molecular structure
- Monitoring chemical reactions
- Testing environmental samples
- Performing quality control analysis
It is especially useful when fast, accurate, and cost-effective analysis is required.
Conclusion
This spectroscopy remains one of the most reliable analytical techniques for studying chemical substances. Its ability to measure light absorption helps scientists identify compounds, determine concentration levels, and ensure quality across industries. From pharmaceutical research to environmental monitoring and food safety testing, UV VIS plays a crucial role in modern science and industrial applications.
As technology advances, This instruments continue improving in accuracy, speed, and portability. Whether used in research laboratories or industrial quality control, UV VIS spectroscopy offers dependable results and valuable chemical insights, making it an essential tool for analytical science.