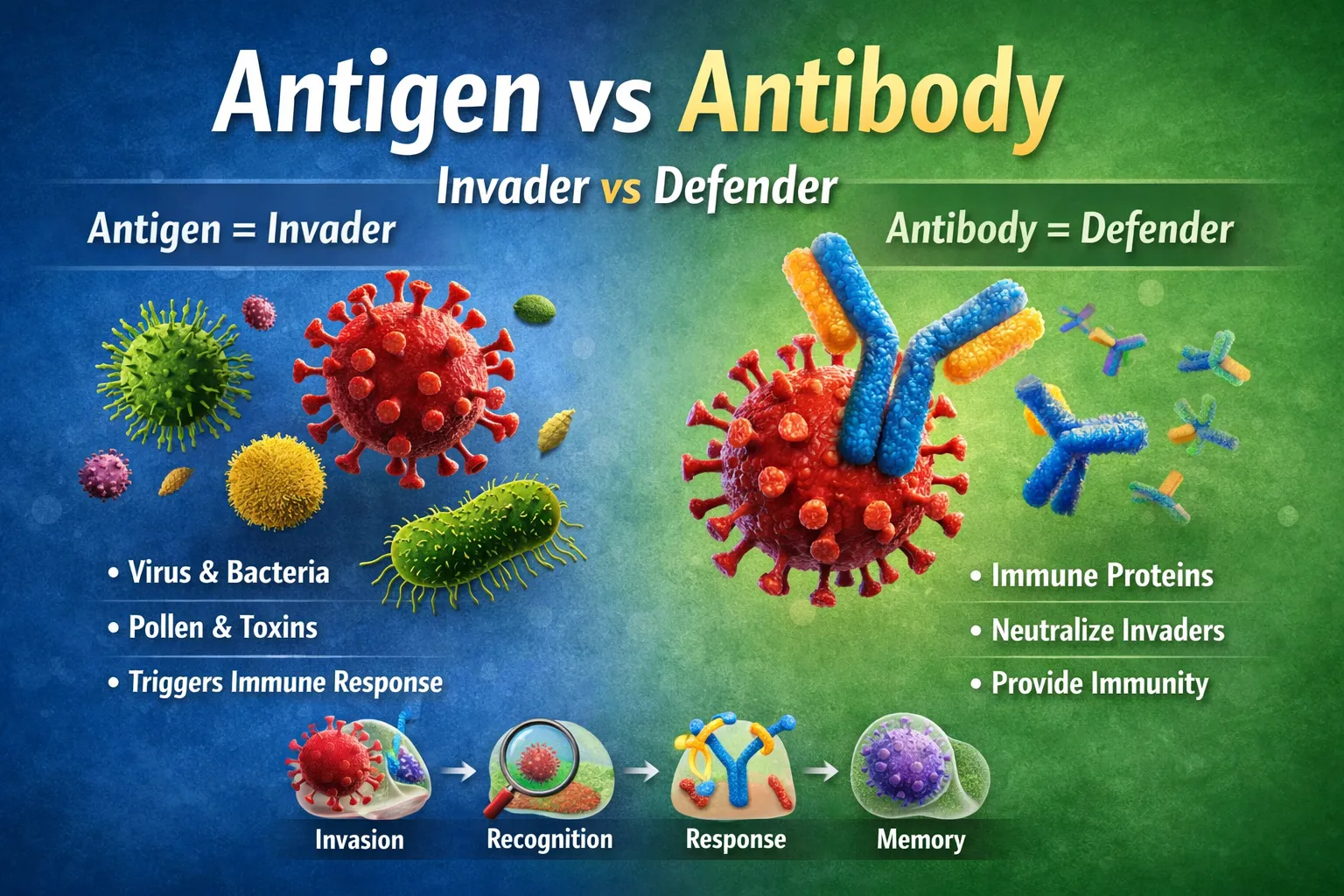
Difference Between Antigen and Antibody
If you want to understand the difference between antigen and antibody, here’s the simplest way to put it:
- Antigen: A foreign substance, like a virus, bacteria, or allergen, that triggers your immune system.
- Antibody: A protein produced by your immune system to neutralize or destroy that antigen.
In short:
Antigen = Invader | Antibody = Defender
This quick explanation sets the stage, but let’s explore the details to fully understand their roles in your body.
Quick Comparison Table: Antigen vs Antibody
| Feature | Antigen | Antibody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Foreign substance that triggers an immune response | Protein produced by the immune system to fight antigens |
| Nature | Usually proteins, polysaccharides, or toxins | Immunoglobulins (proteins) |
| Function | Stimulates the immune system | Neutralizes or destroys antigens |
| Produced by | Pathogens, allergens, foreign cells | B-cells of the immune system |
| Specificity | Each antigen has unique markers | Each antibody is specific to the antigen it targets |
| Examples | Virus particles, bacteria, pollen, transplanted tissue | IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE antibodies |
| Role in Immunity | Triggers immune response | Provides defense and long-term immunity |
What is an Antigen?
An antigen is any substance recognized as foreign by your body. When detected, it activates the immune system to protect you from harm.
Key points about antigens:
- Found on the surface of pathogens, toxins, or foreign cells.
- Can be proteins, polysaccharides, or other molecules.
- Trigger production of antibodies.
- Examples: Influenza virus proteins, COVID-19 spike protein, pollen, bacterial toxins.
Essentially, antigens are the “invaders” that alert your immune system.
What is an Antibody?
An antibody, also called immunoglobulin, is a protein produced by your immune system to fight a specific antigen. Think of it as a custom-made defender for each invader.
Key points about antibodies:
- Produced by B-cells in response to antigens.
- Bind to antigens to neutralize them or mark them for destruction.
- Highly specific to the antigen they target.
- Types of antibodies include:
- IgG: Most common, provides long-term immunity.
- IgM: First responder, short-term protection.
- IgA: Found in mucous membranes and breast milk, protects entry points.
- IgE: Involved in allergies.
- IgD: Helps activate B-cells.
How Antigens and Antibodies Work Together
Understanding their interaction explains immune defense and how vaccines work:
- Invasion: Pathogens enter the body carrying antigens.
- Recognition: Immune system detects the antigens as foreign.
- Response: B-cells produce antibodies specific to the antigen.
- Neutralization: Antibodies bind to antigens, stopping infection.
- Memory: Memory B-cells remain for faster response if the antigen reappears.
This is why vaccines introduce harmless antigens—to prepare your body to fight infections efficiently.
Examples of Antigens and Antibodies
Antigens:
- COVID-19 spike protein
- Influenza virus surface proteins
- Pollen
- Bacterial toxins
Antibodies:
- COVID-19 IgG antibody
- Anti-pollen IgE antibodies
- Hepatitis B antibody
Why Knowing the Difference Matters
Understanding antigens and antibodies is crucial in healthcare and daily life:
- Vaccines: Help your body produce antibodies without causing illness.
- Disease detection: Antibody tests indicate current or past infections.
- Allergy management: Identify antigens causing reactions.
- Transplant medicine: Monitor antigen-antibody interactions to prevent organ rejection.
This knowledge has real-world applications in medicine, immunology, and public health.
Quick Facts to Remember
- Antigen = Invader
- Antibody = Defender
- Antigens trigger the immune response; antibodies neutralize antigens.
- Each antibody is highly specific to its antigen.
FAQ (Featured Snippet Boost)
Q: What is the main difference between antigen and antibody?
A: Antigens are foreign substances that trigger the immune system, while antibodies are proteins that neutralize or destroy those antigens.
Q: Can antibodies attack all antigens?
A: No, antibodies are highly specific and only target the antigen they are designed to recognize.
Q: How do vaccines work with antigens and antibodies?
A: Vaccines introduce harmless antigens so your body can produce antibodies and develop immunity without causing illness.
Q: What types of antibodies are there?
A: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD, each with a unique role in protecting the body.
Takeaway
The difference between antigen and antibody is foundational to understanding immunity. Antigens are foreign invaders that trigger your immune system, while antibodies are the body’s specialized defense proteins. Their interaction explains why vaccines, immune responses, and antibody tests are effective tools in modern healthcare.
By knowing their roles, you can better understand how your body fights infections, develops immunity, and responds to vaccines or allergens.
More here : Antibodies vs Antigens